‘My child had an unstoppable crying spell last night due to pain in his ear. I think he has contracted an ear infection yet again after his last treatment.’
An ear infection is most commonly referred to as Otitis Media in layman terms. As a parent or a healthcare novice, you will be able to identify a frequent association between otitis media and children. If your child indicates any ear-related disease, you must immediately contact the Best ENT Specialist in Islamabad for medical advice.
What is Otitis Media?
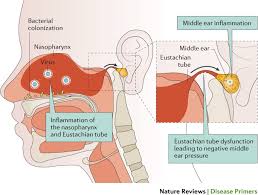
Otitis media refers to a group of inflammatory diseases that affect the middle ear cavity and its components. Ranging from Acute Otitis Media (AOM), Otitis Media with Effusion (OME), Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM), and Adhesive Otitis Media; this disease has multiple types.
What Causes It?
The pathogenesis of Otitis Media is determined by a variety of host, infectious, environmental, and genetic aspects. Approximately, 95 percent of bacterial ear infections can be attributed to the following infective agents:
- Streptococcus pneumonia
- Haemophilus influenza
- Moraxella catarrhalis
If the ear infection is of viral origin, the most probable species would include:
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Influenza viruses
- Parainfluenza viruses
- Rhinovirus
- Adenovirus
Who is Most Likely to Contract This Infection: Risk Factors
If you are exposed to a cold climate, changing weather, or shifting altitudes, you have chances to develop an ear infection.
In the case of children, the age window of 6 to 36 months is the most susceptible of all. Attending daycare, dependence on a pacifier, and exposure to polluted air can predispose your child to contract the infection. Bottle-fed babies are more vulnerable as they consume it while lying down, this position can cause leakage into the ear cavity.
Besides, if you have a history of impaired immunity due to conditions like renal insufficiency or AIDS, you might be at a greater risk of contracting Otitis Media. Vitamin A deficiency in youngsters and obesity in adults are equally responsible host variables that accelerate the progression of infection.
How Will My Child Present With Otitis Media: Clinical Features
- Earache
- Interrupted sleep due to pain
- Irritability
- A feeling of fullness in the ear
- Loss of appetite to avoid pain while swallowing (altering internal pressures can aggravate the pain)
- White, yellow, or a brown exudate (indicates a ruptured tympanic membrane)
- Transient hearing loss (fluid accumulation can interfere with nerve signal transmission)
- Some non-specific symptoms include headache, neck pain, fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and balance problems.
Complications
- Bacterial abscess (pus collection)
- Bacterial meningitis (inflamed meninges)
- Cholesteatoma (abnormal skin growth behind the eardrum due to a chronic infection)
- Cholesterol granuloma (benign, fluid-filled, and cholesterol-containing cyst)
- Conductive and sensorineural hearing loss (fluid build-up distorts the nerve supply)
- Dural sinus thrombosis
- Facial paralysis (fluid build-up disturb the nerve supply)
- Infectious eczematoid dermatitis (ear eczema)
- Labyrinthitis
- Mastoiditis
- Otitic hydrocephalus (rare intracranial complication independent of hydrocephalus)
- Perforation of tympanic membrane
- Petrositis
- Subdural empyema (suppurative collection between the meninges)
- Tympanosclerosis (scarring of eardrum due to persistent inflammation)
Otitis media is a primary cause of infant and childhood mortality in underdeveloped countries hence contacting the Best ENT Specialist in Lahore is a must if your child conforms to the aforementioned criteria of Otitis Media at any point.